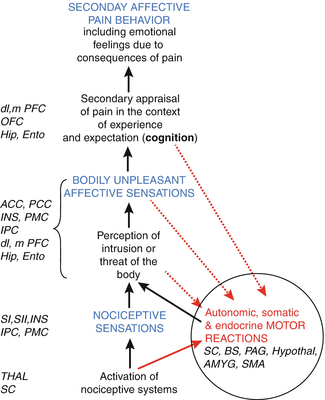
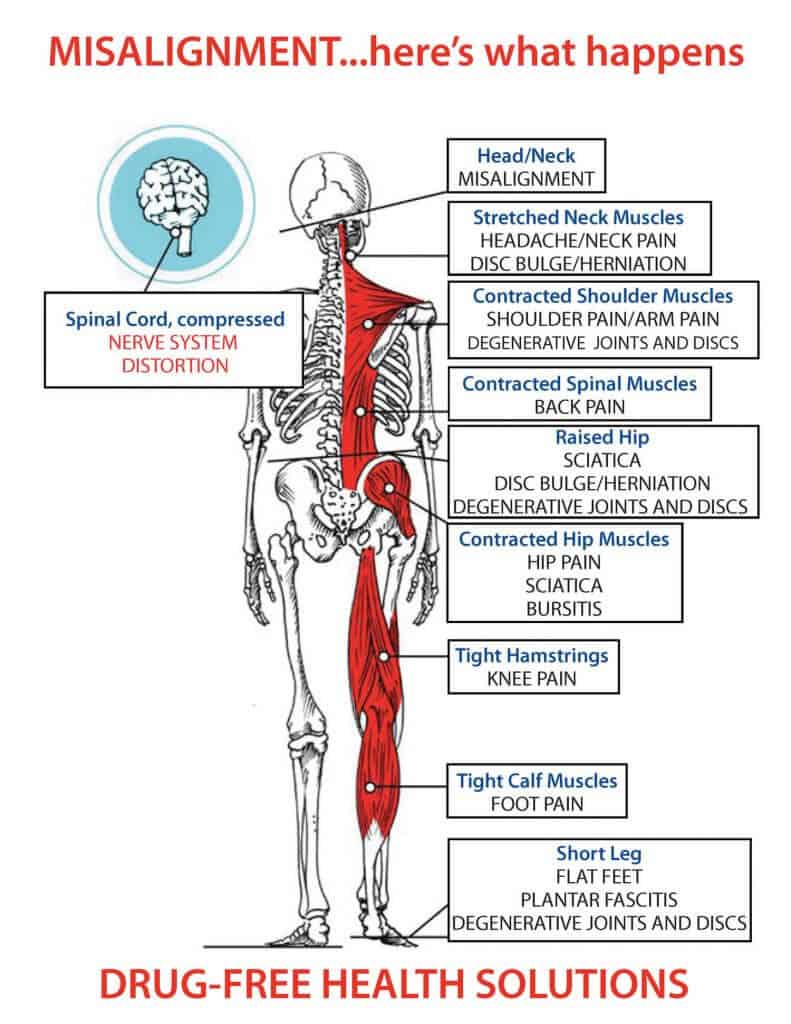
Sympathetic Nervous System Pain
Sympathetic nervous system pain. The parasympathetic division has craniosacral outflow meaning that the neurons begin at the cranial nerves specifically the oculomotor nerve facial nerve. Both systems are continuously producing a response however this balancing act can be tipped in one direction or another based on the current physiological state of that individual or what is occurring around their surroundings. The central nervous system and.
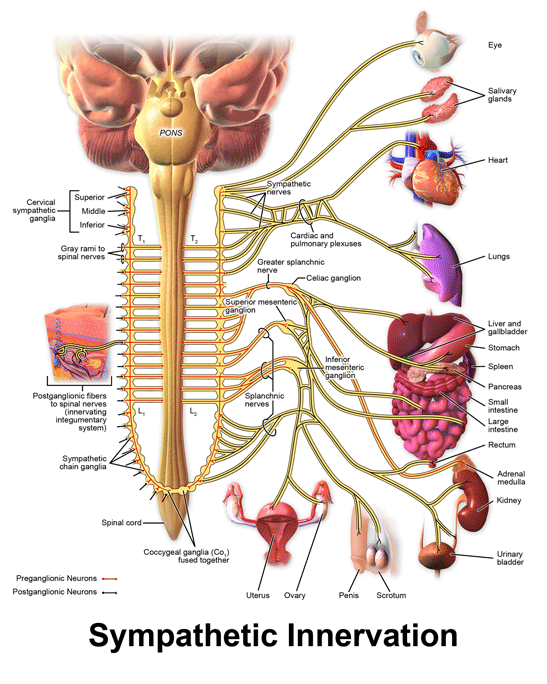
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for regulating many homeostatic mechanisms in living organisms. This means theyre responsible for helping you maintain your resting heart rate. It takes in information through our senses processes the information and triggers reactions such as making your muscles move or causing you to feel pain.
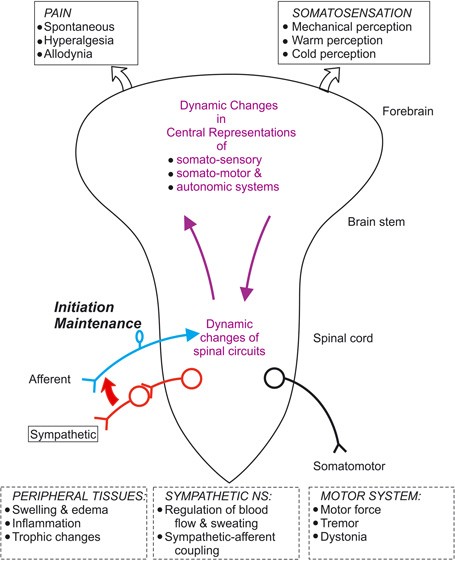
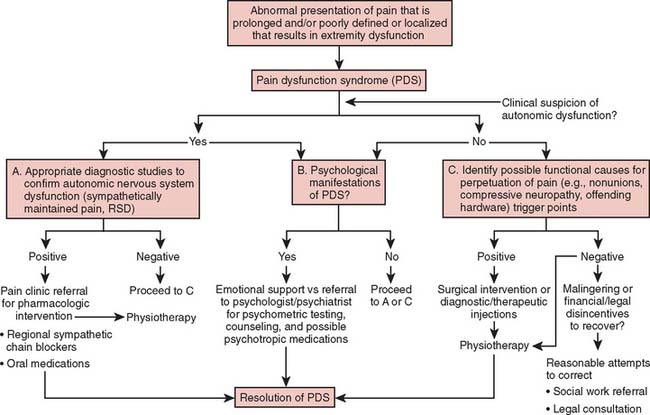
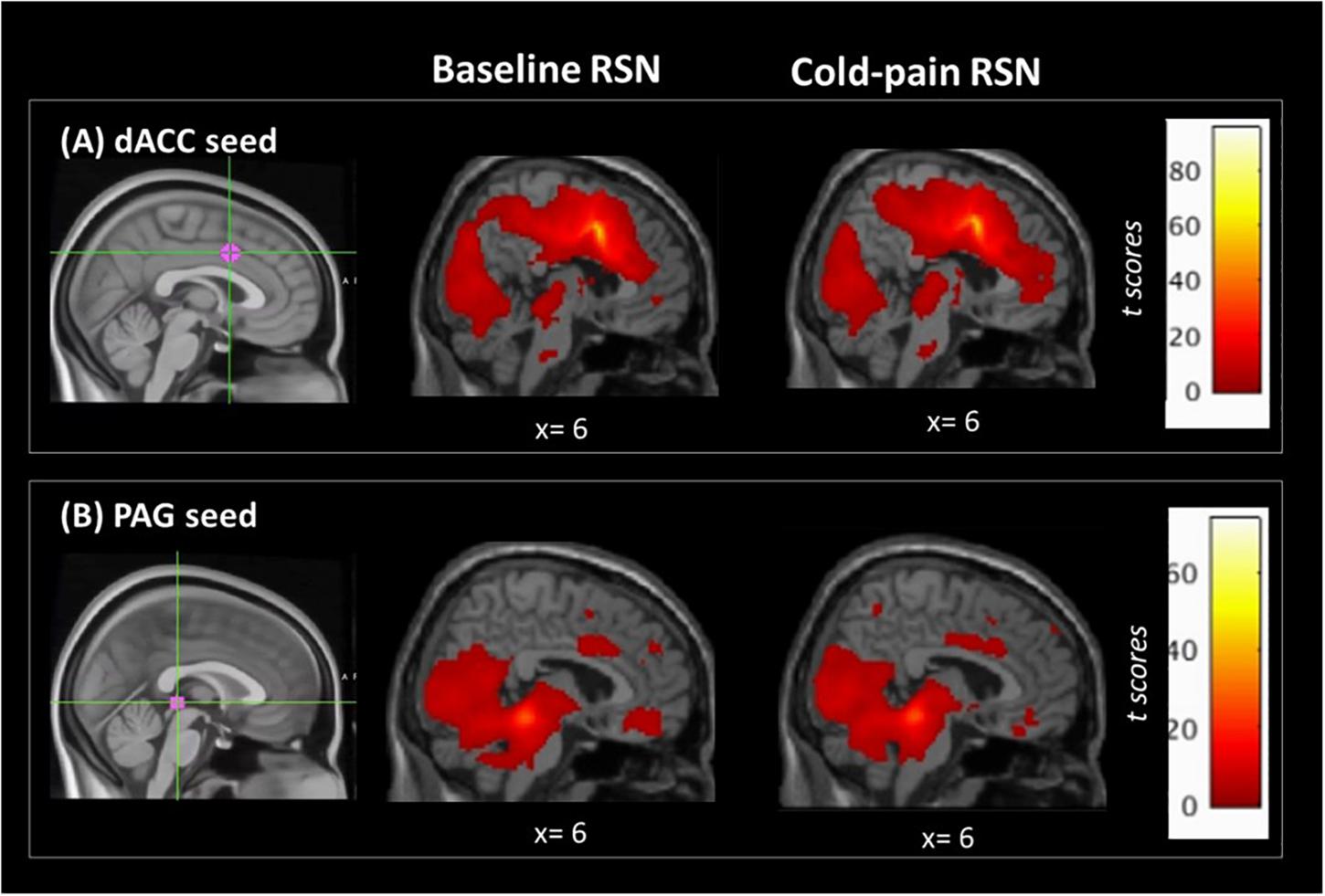
This is often used in pain studies as humans can tolerate it everyone has experienced cold hands before it is not scary and does not result in psychological damage and is a a good model stimulus easy to replicate in labs around the world. If you feel pain from stimuli that dont usually cause pain you might have allodynia. It allows you to do things like walk speak swallow breathe and learn and controls how your body reacts in an emergency.
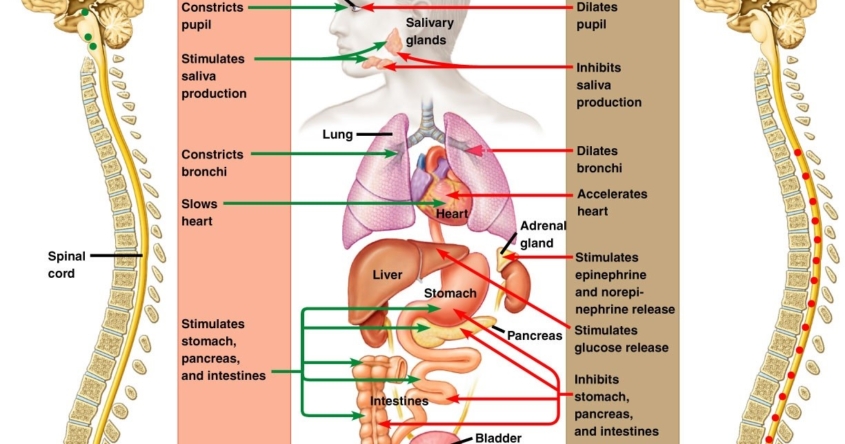
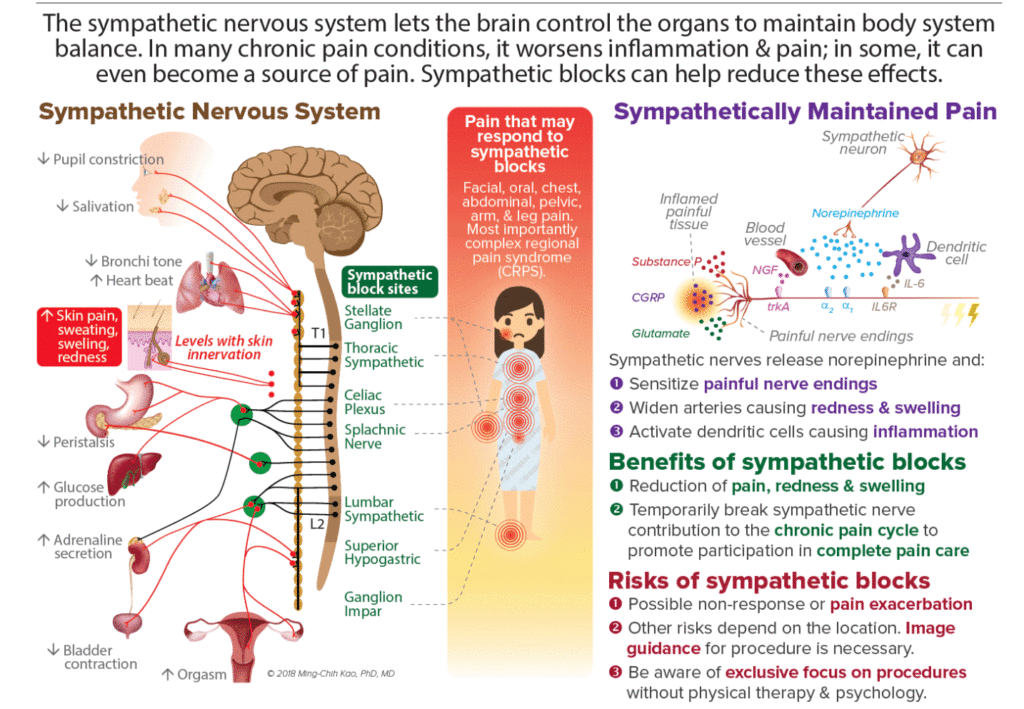
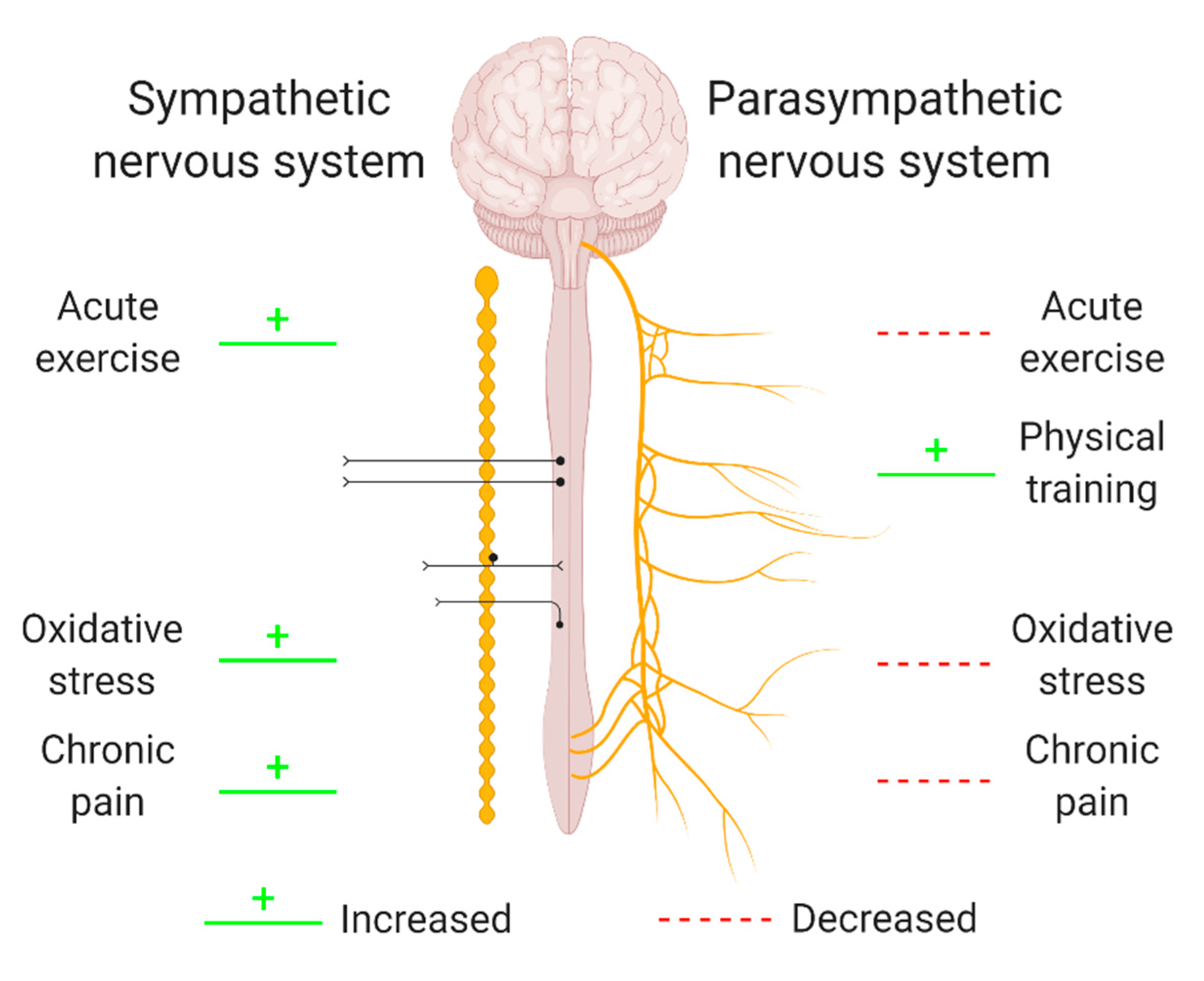
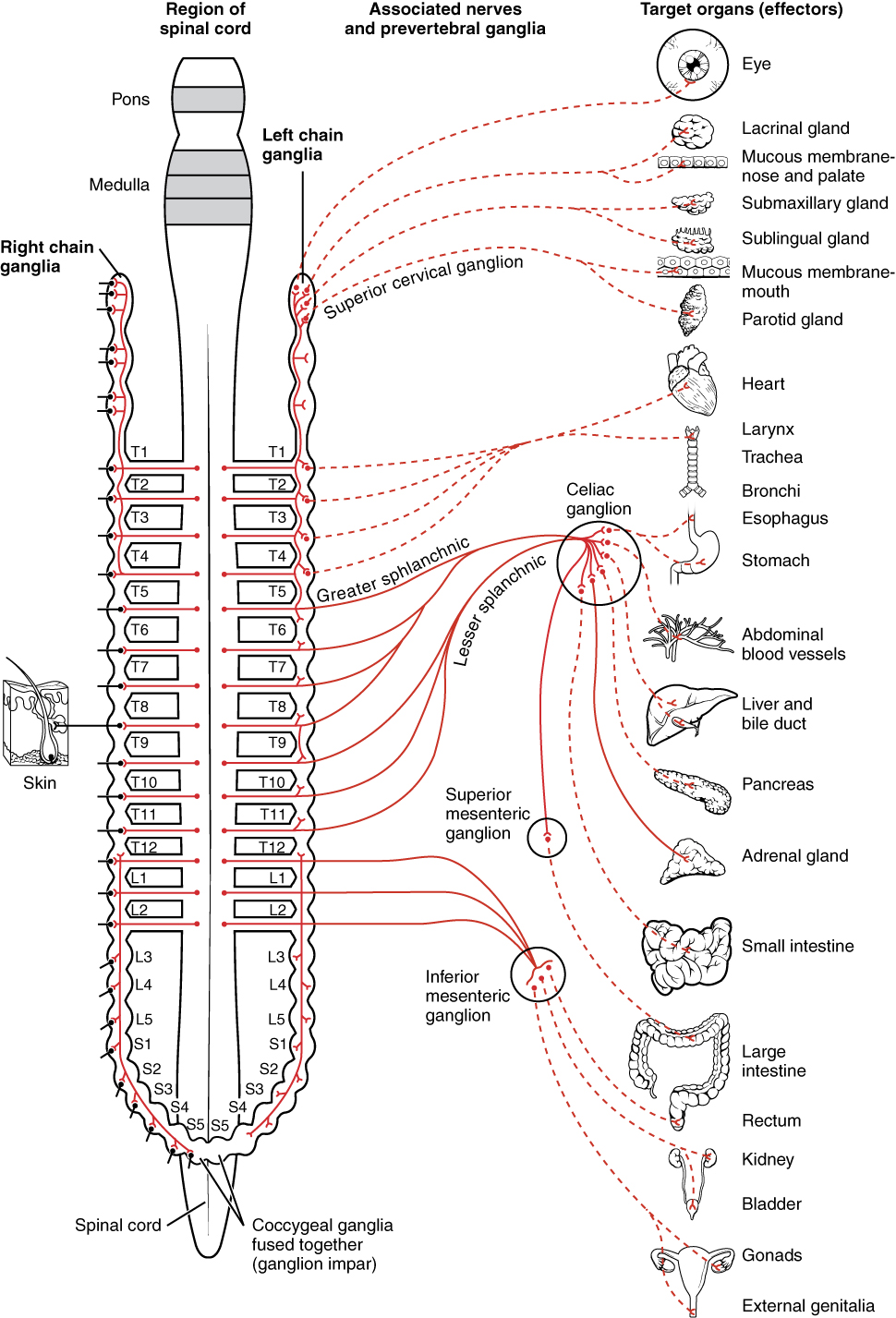
The sympathetic nervous system tells the body to get ready for physical and mental activity. These hormones are called epinephrine and norepinephrine which help your body perform optimally during such events. The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous systemThe sympathetic division emerges from the spinal cord in the thoracic and lumbar areas terminating around L2-3.
For most people the resting heart rate is between 60. Fibers from the SNS innervate tissues in almost every organ system and provide physiological regulation over diverse body processes including pupil diameter gut. The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The overall effect of the sympathetic system under these conditions is to prepare the body for strenuous physical activity. Human nervous system system that conducts stimuli from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord and conducts impulses back to other body parts. In contrast to the arrangement in the sympathetic nervous system there is little divergence in the parasympathetic nervous system.
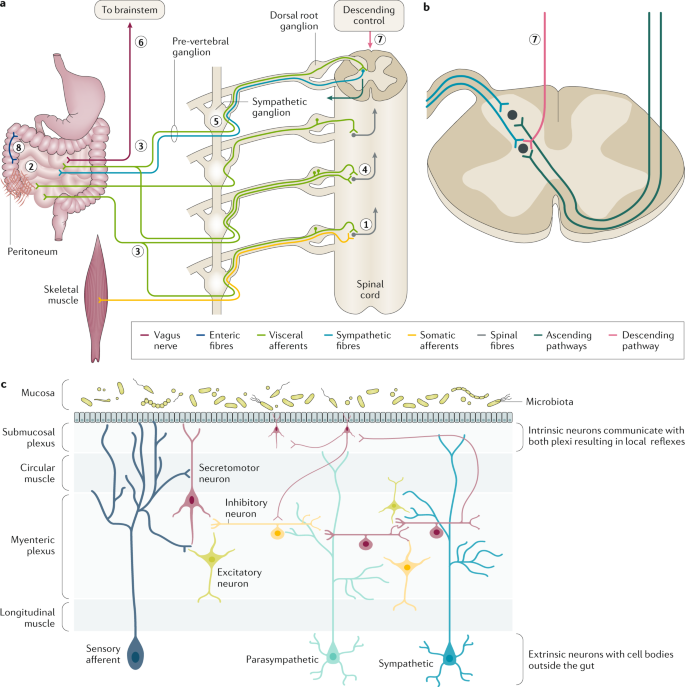
The parasympathetic nervous system is characterized by long preganglionic and very short postganglionic nerves and with only a few exceptions an absence of well-defined anatomically distinct ganglia. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system and sometimes considered an independent system.
The central nervous system includes the spinal cord and the brain.
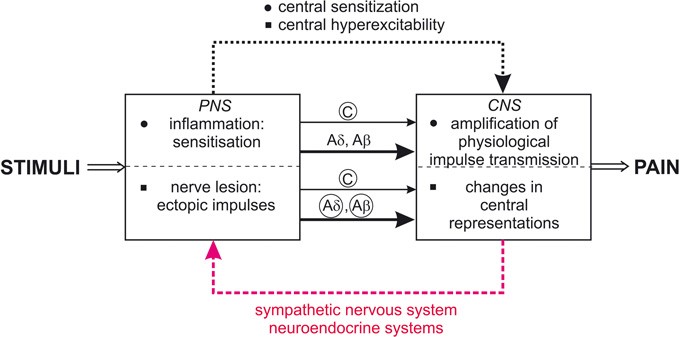
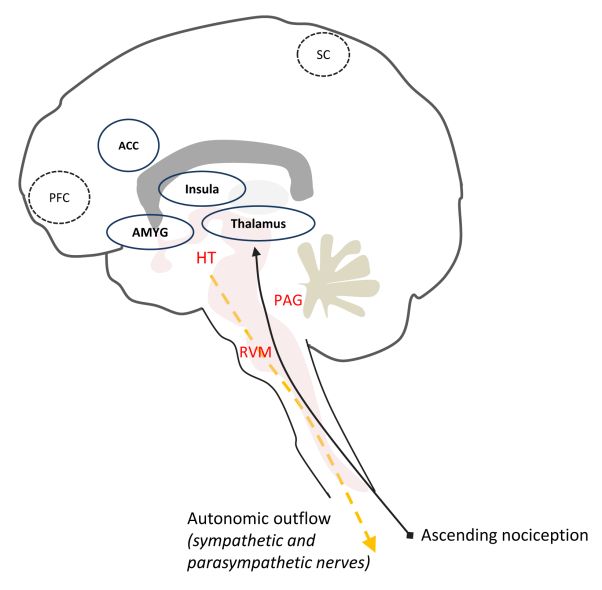
Both systems are continuously producing a response however this balancing act can be tipped in one direction or another based on the current physiological state of that individual or what is occurring around their surroundings. In contrast to the arrangement in the sympathetic nervous system there is little divergence in the parasympathetic nervous system. For most people the resting heart rate is between 60. The sympathetic nervous system releases two hormones within the body in response to stress resulting in an adrenaline rush or a sense of urgency that occurs during stressful conditions. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system and sometimes considered an independent system. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for fight or flight responses and maintains homeostasis during daily activities such as exercise eating a meal or regulation of body. The term autonomic nervous system ANS refers to collections of motor neurons ganglia situated in the head neck thorax abdomen and pelvis and to the axonal connections of these neurons Figure 1Autonomic pathways together with somatic motor pathways to skeletal muscle and neuroendocrine pathways are the means whereby the central nervous system CNS sends. The brain is divided into 3 main sectionsthe brain stem which controls many basic life functions the cerebrum which is the center of conscious decision-making and the cerebellum which is involved in movement and motor controlThe spinal cord of dogs is divided into regions that correspond to the vertebral bodies the. The central nervous system and.
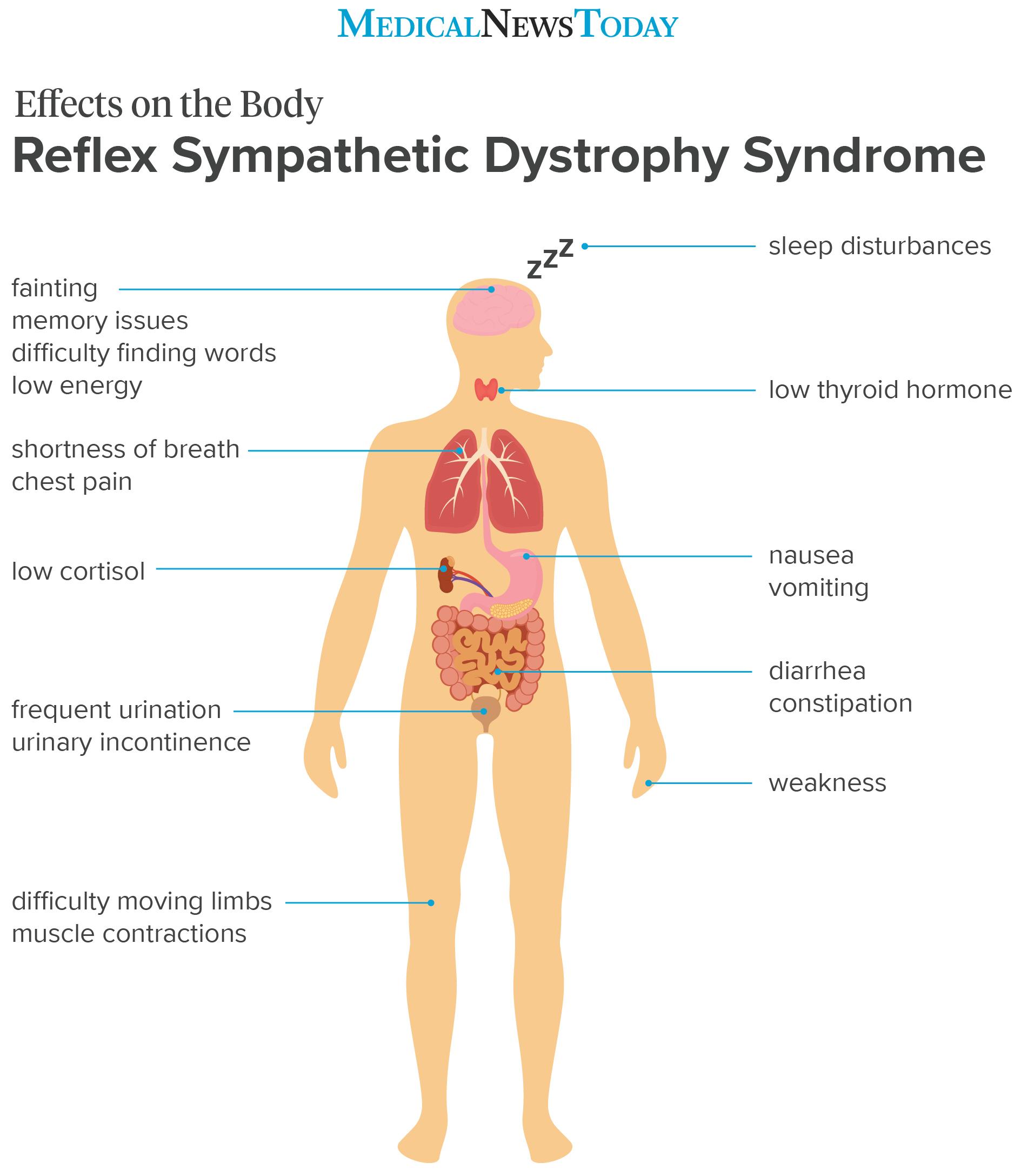
Chronic fatigue anxiety chronic pain burnout the list goes on and on. The enteric nervous system ENS is a branch of the ANS which operates independently of the central nervous systemThis system consists of neurons which are confined to the gastrointestinal tract also known as the gut. Sympathetic nervous system diagram The autonomic system is made up of two divisions the sympathetic and parasympathetic systemsThey usually work antagonistically in the organs but in a well integrated manner. Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions are involved in sexual activity as are the parts of the nervous system that control voluntary actions and transmit sensation from the skin somatic nervous system Somatic nervous system The peripheral nervous system consists of more than 100 billion nerve cells neurons that run throughout the body like strings making connections with the. In contrast to the arrangement in the sympathetic nervous system there is little divergence in the parasympathetic nervous system. The term autonomic nervous system ANS refers to collections of motor neurons ganglia situated in the head neck thorax abdomen and pelvis and to the axonal connections of these neurons Figure 1Autonomic pathways together with somatic motor pathways to skeletal muscle and neuroendocrine pathways are the means whereby the central nervous system CNS sends. The parasympathetic nervous system is characterized by long preganglionic and very short postganglionic nerves and with only a few exceptions an absence of well-defined anatomically distinct ganglia.

















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14062/gnEvUC2kgTFXvmrjP39Yw_Sympathetic_nervous_system.png)










Post a Comment for "Sympathetic Nervous System Pain"